10 Mysterious Lost Civilizations That Will Amaze You
10 Mysterious Lost Civilizations That Will Amaze You
Lost civilizations have always fascinated historians, archaeologists, and curious minds. These ancient societies shaped our world and then disappeared, leaving behind ruins, mysteries, and unanswered questions. In this guide, we explore 10 remarkable lost civilizations that still capture global imagination.
Table of Contents
- What Are Lost Civilizations?
- The Indus Valley Civilization
- Göbekli Tepe
- The Nabta Playa People
- The Chachapoya — The Cloud People
- The Sea Peoples
- The Minoans
- The Olmecs
- The Cucuteni–Trypillia Culture
- The Hittite Empire
- The Ancestral Puebloans
- Why Lost Civilizations Matter Today
What Are Lost Civilizations?
Lost civilizations refer to ancient societies that once flourished but eventually disappeared due to war, climate change, natural disasters, or cultural collapse. Their ruins, artifacts, and legends help us understand how early humans lived, built, and evolved.

1. The Indus Valley Civilization
The Indus Valley Civilization was one of the world’s earliest urban cultures, known for its advanced city planning, drainage systems, and trade networks. Cities like Mohenjo-daro and Harappa showed remarkable engineering skills long before modern times.

2. Göbekli Tepe
Göbekli Tepe in modern-day Turkey is considered the world’s oldest known temple, built over 11,000 years ago. Its massive stone pillars and mysterious carvings challenge everything we know about early human society.

3. The Nabta Playa People
Nabta Playa, located deep in the Sahara Desert, was once home to an advanced prehistoric culture that built one of the world’s earliest known astronomical sites—older than Stonehenge.

4. The Chachapoya — The Cloud People
The Chachapoya lived in Peru’s cloud forests, building stone structures in high cliffs and mountains. Their isolated cities and mysterious mummies have fascinated archaeologists for decades.
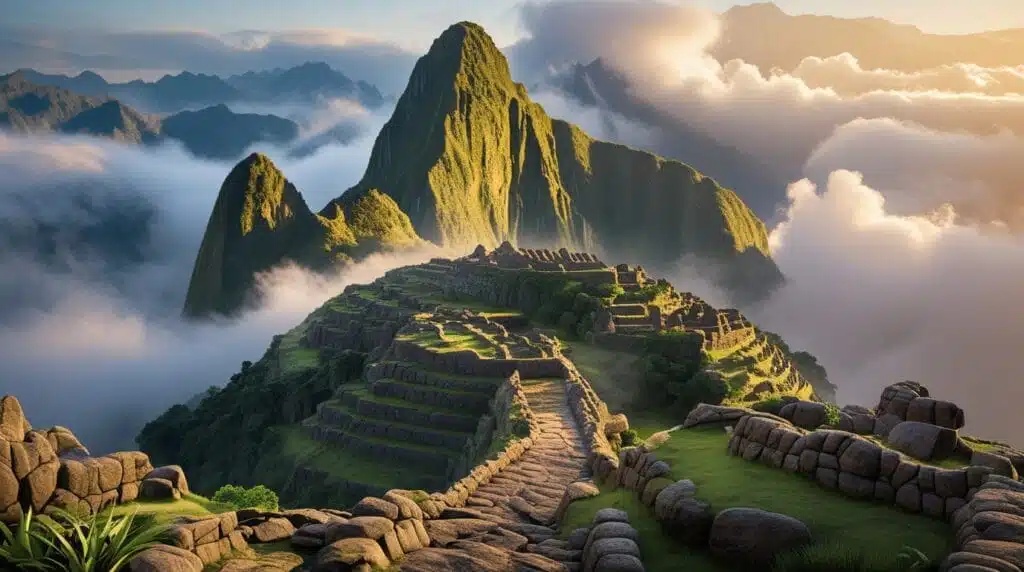

5. The Sea Peoples
The Sea Peoples were powerful naval warriors who attacked ancient Mediterranean civilizations during the Bronze Age collapse. Their exact origins remain unknown, making them one of history’s greatest mysteries.

6. The Minoans
The Minoans lived on the island of Crete and are known for their palaces, frescoes, and advanced art. Their sudden disappearance is often linked to natural disasters, including volcanic eruptions and tsunamis.

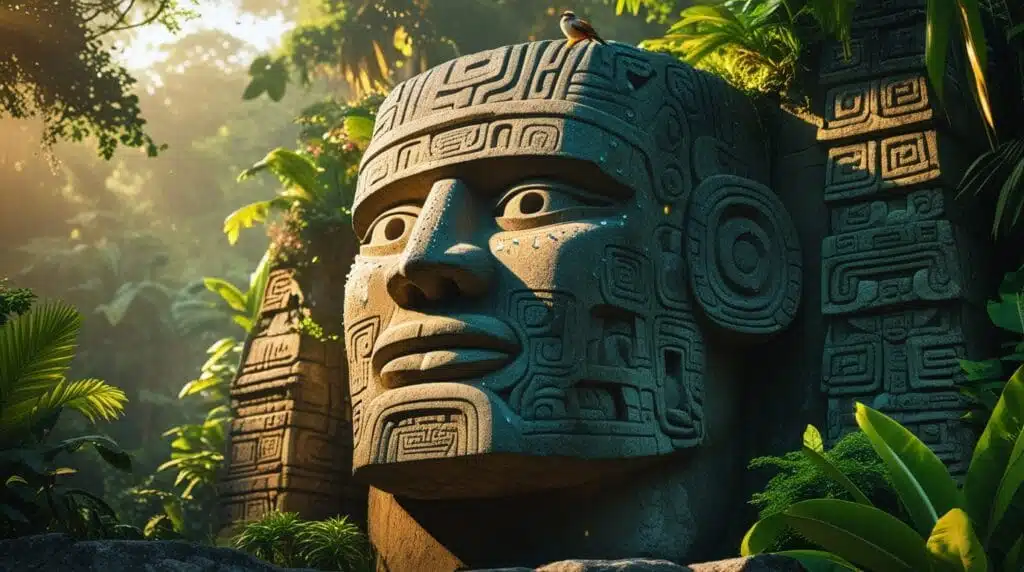
7. The Olmecs
The Olmecs were one of the earliest civilizations in the Americas. They are famous for their giant stone heads and early artwork, which influenced later Mesoamerican cultures like the Maya.

8. The Cucuteni–Trypillia Culture
This ancient European civilization built some of the world’s earliest large settlements. They created unique pottery with spiral designs and practiced early forms of organized city life.

9. The Hittite Empire
The Hittites dominated Anatolia and were one of the first civilizations to use iron weapons. Their empire fell suddenly, leaving behind impressive ruins and historical records.

10. The Ancestral Puebloans
The Ancestral Puebloans built incredible cliff dwellings in North America. Their stone homes protected them from enemies and harsh climates, yet the reason for their disappearance remains unclear.

Why Lost Civilizations Matter Today
Lost civilizations teach us about human resilience, creativity, and innovation. Their achievements inspire modern architecture, engineering, and cultural studies. By studying them, we connect with the deeper story of human history.

Final Thoughts: Ancient Knowledge Lost?
The ancient Roman aqueducts stand as a powerful reminder of how innovation, engineering brilliance, and long-term vision shaped entire civilizations. Their massive arches, precise gradients, and the sheer scale of construction reflect the ingenuity of a society determined to master nature and ensure the prosperity of its people.
Even thousands of years later, these monumental structures continue to inspire architects, engineers, historians, and curious minds who seek to understand how such advanced technology emerged in an age without modern machinery. The legacy of Roman aqueducts lives not only in the ruins that still dominate landscapes across Europe but also in the water systems and engineering principles that modern cities still rely on today.
By studying these ancient masterpieces, we gain a deeper appreciation for the resilience and intelligence of early civilizations — and a clearer perspective on how the achievements of the past continue to influence the world we live in. The story of Roman aqueducts is ultimately a story of human determination and creativity, a testament to what becomes possible when a society dares to think beyond its limitations and build for the future.
While the aqueducts are often admired for their impressive appearance, their true value lies in what they accomplished for everyday Roman life. These waterways supported public baths, fountains, private homes, gardens, and even entire industries that depended on a steady water supply. They also helped maintain public health by preventing water shortages and reducing contamination. By providing such a reliable system, the Romans created the foundation for a thriving urban culture that became the heartbeat of their empire.
Understanding how these systems were designed and maintained gives us a clearer picture of the Roman world and reminds us that progress often begins with solving simple but essential human needs. The aqueducts were more than structures — they were lifelines that sustained one of history’s greatest civilizations.

In 2024, a team of archaeologists made a discovery that could change everything: they found a lost city beneath the pyramids.
Click Below To Watch Full Story
https://www.youtube.com/@EchoesofAntiquity-egypt/videos
-
10 Forbidden Archaeological Discoveries That Scientists Can’t Explain
10 Forbidden Archaeological Discoveries That Scientists Can’t Explain Introduction Human history is supposed to follow a simple timeline:primitive → advanced → modern.But…
-
The Ancient Robots: Did Lost Civilizations Build Machines Before Modern Times?
What if ancient civilizations built Ancient Robots thousands of years before modern technology even existed? It sounds like science fiction—but ancient texts,…
-
Ancient Supercomputers? The Mysterious Devices That Shouldn’t Exist
Table of Contents Introduction: Ancient Tech Beyond Imagination What if we told you that some ancient civilizations may have created technology so…
-
The Ancient Sound Weapons: Did Lost Civilizations Master Sonic Warfare?
Introduction Ancient Sound Weapons What if ancient civilizations possessed weapons so advanced, they could shatter stone walls—or even minds—using nothing but sound?…
-
They Found a Lost City Beneath the Pyramids… And It Changes Everything We Know About History
🌍 Table of Contents 🏛️ Introduction: A Hidden City Awakes For generations, the Great Pyramids of Giza have captivated the world. But…
-
Ancient Engineering Marvels: 7 Epic Megastructures That Defined Civilization
Table of Contents Introduction Throughout history, civilizations have showcased their brilliance through awe-inspiring architectural and engineering feats. These Ancient Engineering Marvels continue…