Ancient Engineering Marvels: 7 Epic Megastructures That Defined Civilization
Table of Contents
- Introduction of Ancient Engineering Marvels
- The Great Pyramid of Giza
- The Roman Colosseum
- The Great Wall of China
- Petra’s Rock-Cut Architecture
- The Aqueducts of Rome
- Machu Picchu’s Terracing System
- The Hagia Sophia’s Dome
- Conclusion

Introduction
Throughout history, civilizations have showcased their brilliance through awe-inspiring architectural and engineering feats. These Ancient Engineering Marvels continue to amaze historians, archaeologists, and engineers alike. From precision-cut stones to advanced water systems, these structures demonstrate a level of sophistication that was ahead of their time. Let’s explore seven megastructures that changed history and continue to inspire modern engineering.
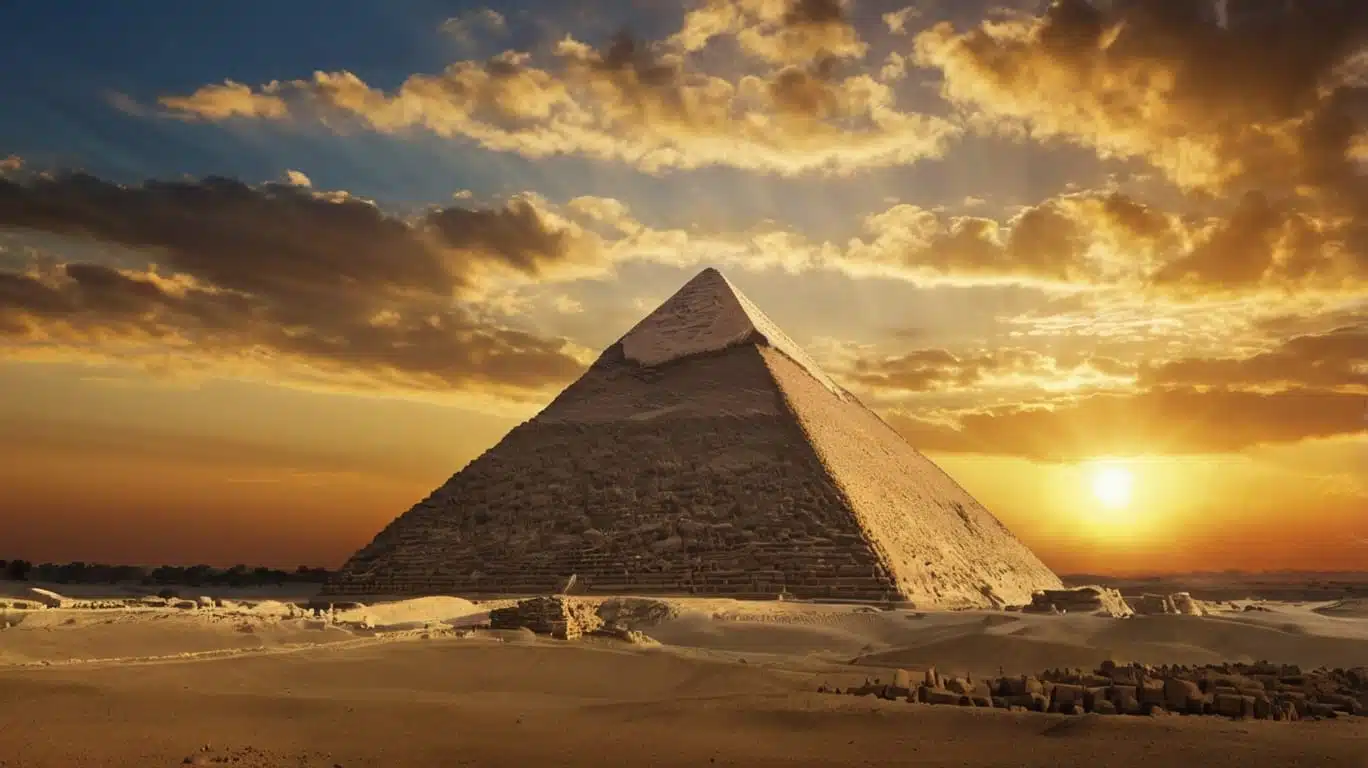
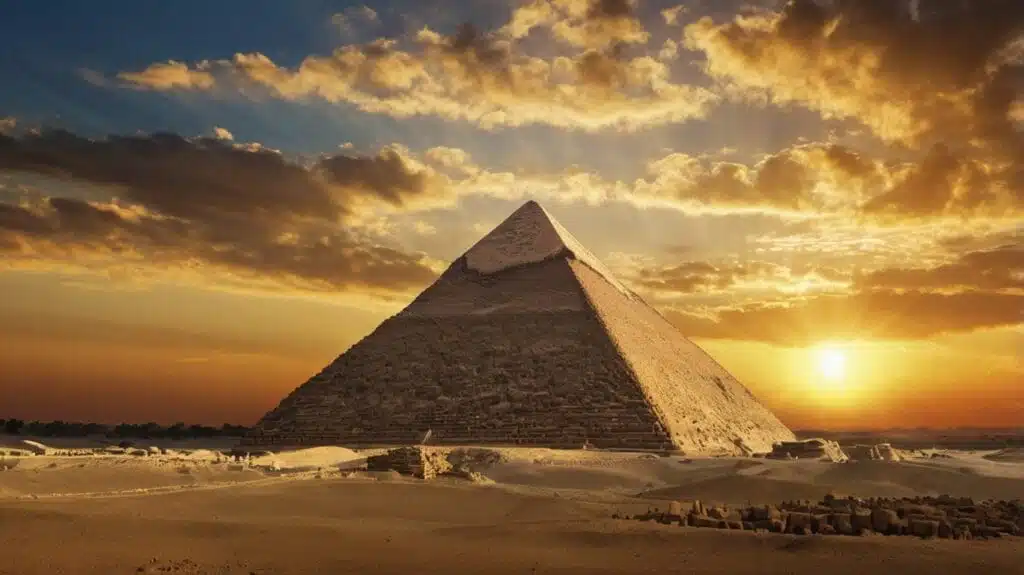
1. The Great Pyramid of Giza
Built: c. 2580–2560 BCE
Location: Egypt
The Great Pyramid of Giza stands as the last surviving wonder of the ancient world. Its precision-cut limestone blocks, mathematical alignments, and sheer scale make it a testament to the ingenuity of the ancient Egyptians. Despite centuries of study, historians still debate how it was constructed with such accuracy.

2. The Roman Colosseum
Built: 70–80 CE
Location: Rome, Italy
The Colosseum is an iconic symbol of Roman engineering. This massive amphitheater, capable of holding up to 50,000 spectators, featured advanced design elements such as retractable awnings, underground tunnels, and tiered seating. It was used for gladiator battles, public spectacles, and theatrical performances.

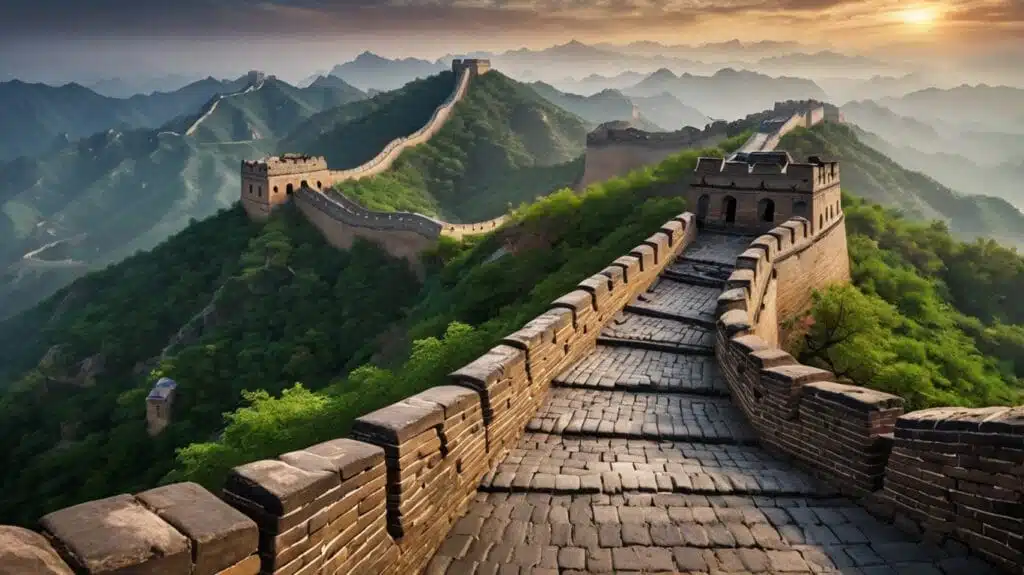
3. The Great Wall of China
Built: 7th century BCE – 17th century CE
Location: China
Stretching over 13,000 miles, the Great Wall of China is one of the most ambitious engineering projects in history. It was constructed to protect against invasions and served as a massive transportation and communication route. The Wall’s watchtowers, fortresses, and layered defense systems showcase strategic brilliance.

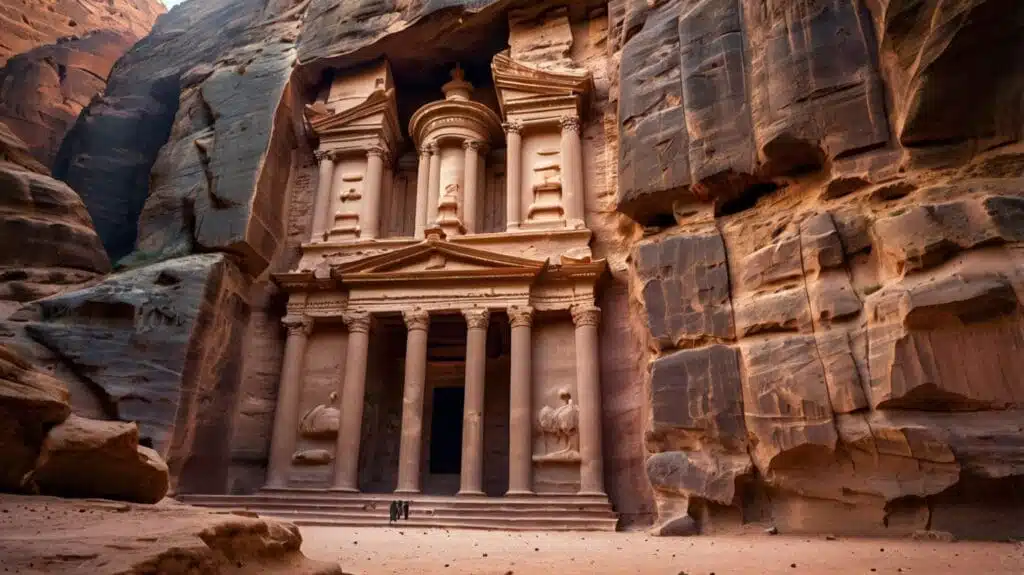
4. Petra’s Rock-Cut Architecture
Built: c. 4th century BCE
Location: Jordan
The city of Petra is an architectural wonder carved directly into rose-red sandstone cliffs. The Nabataeans engineered an advanced water management system, allowing the city to thrive in the desert. The Treasury and Monastery remain some of the finest examples of ancient craftsmanship.

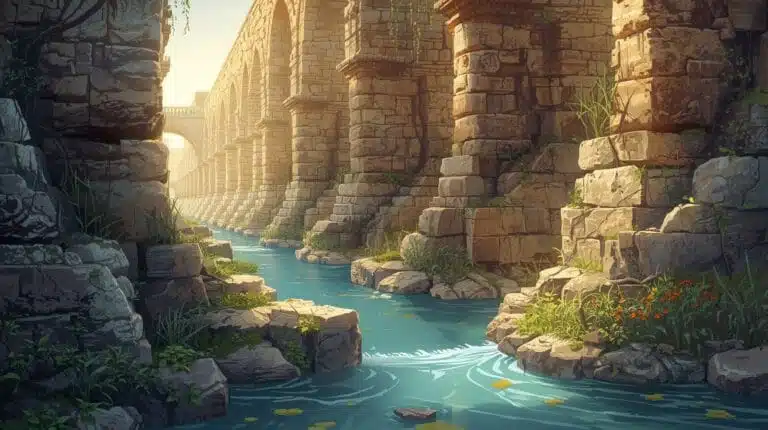
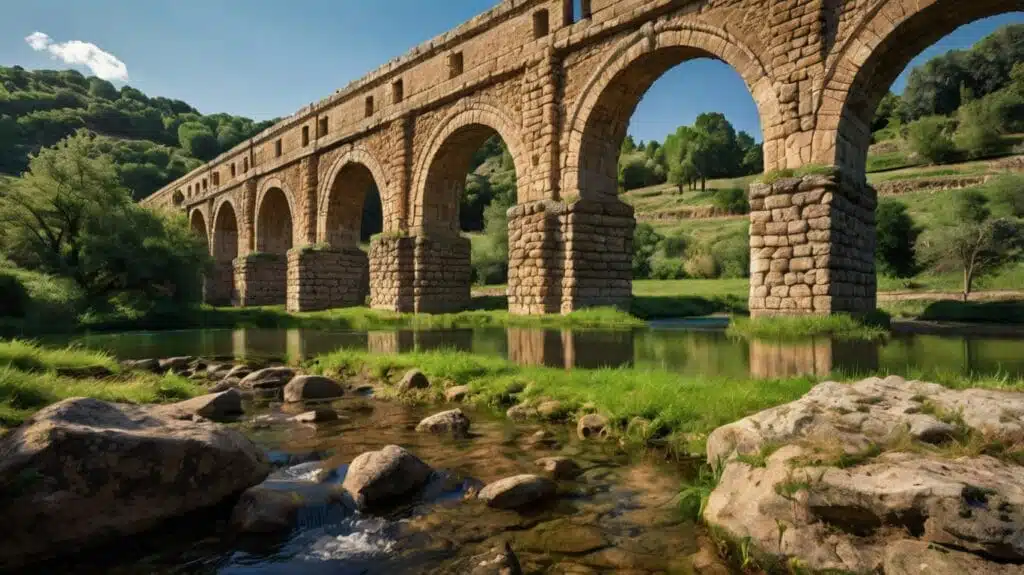
5. The Aqueducts of Rome
Built: c. 312 BCE onwards
Location: Rome, Italy
The Roman aqueducts revolutionized urban infrastructure by supplying cities with clean water through an extensive network of stone and concrete channels. These aqueducts used gravity-based flow and showcased Rome’s mastery of civil engineering.

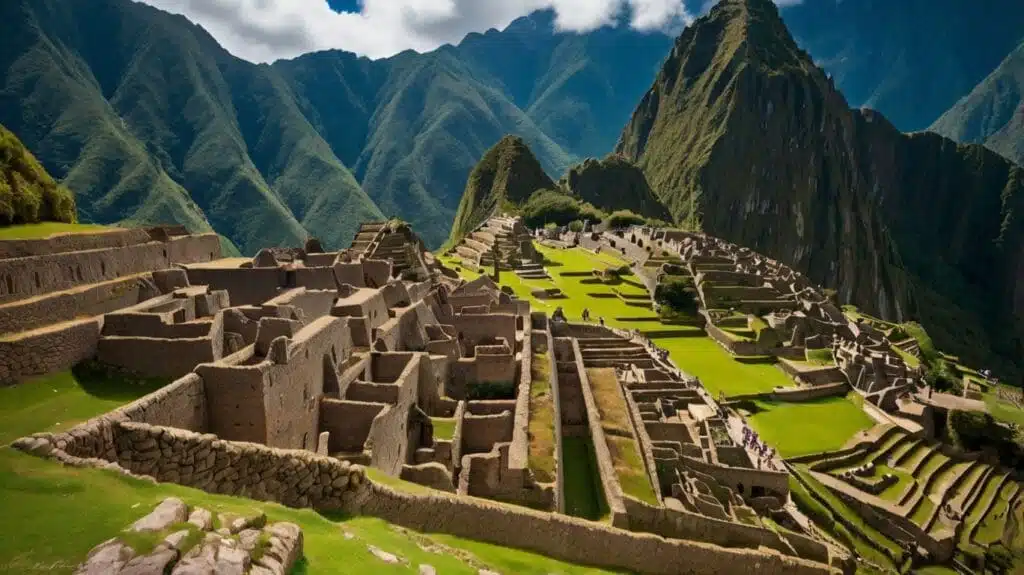
6. Machu Picchu’s Terracing System
Built: c. 1450 CE
Location: Peru
The Incan citadel of Machu Picchu is famous for its sophisticated terracing system, which prevented soil erosion and optimized agricultural productivity. These terraces, along with the site’s earthquake-resistant structures, demonstrate the Incas’ deep understanding of their environment.

7. The Hagia Sophia’s Dome
Built: 537 CE
Location: Istanbul, Turkey
The Hagia Sophia is a masterpiece of Byzantine architecture, featuring a massive central dome that appears to float above its vast interior. Its innovative structural support system influenced countless religious buildings worldwide.

Conclusion
These Ancient Engineering Marvels showcase humanity’s relentless pursuit of innovation. From massive stone pyramids to sophisticated water systems, these structures continue to inspire architects and engineers today. They remind us that great civilizations were not only builders but also visionaries who shaped the course of history.
What lost ancient city fascinates you the most? Let us know in the comments!
(Interested in more ancient wonders? Read our post on 6 Secrets of Ancient Civilizations That Will Blow Your Mind)
Click Below To Watch Full Story
https://www.youtube.com/@EchoesofAntiquity-egypt/videos
-
10 Forbidden Archaeological Discoveries That Scientists Can’t Explain
10 Forbidden Archaeological Discoveries That Scientists Can’t Explain Introduction Human history is supposed to follow a simple timeline:primitive → advanced → modern.But…
-
10 Mysterious Lost Civilizations That Will Amaze You
10 Mysterious Lost Civilizations That Will Amaze You Lost civilizations have always fascinated historians, archaeologists, and curious minds. These ancient societies shaped…
-
The Ancient Robots: Did Lost Civilizations Build Machines Before Modern Times?
What if ancient civilizations built Ancient Robots thousands of years before modern technology even existed? It sounds like science fiction—but ancient texts,…
-
Ancient Supercomputers? The Mysterious Devices That Shouldn’t Exist
Table of Contents Introduction: Ancient Tech Beyond Imagination What if we told you that some ancient civilizations may have created technology so…
-
The Ancient Sound Weapons: Did Lost Civilizations Master Sonic Warfare?
Introduction Ancient Sound Weapons What if ancient civilizations possessed weapons so advanced, they could shatter stone walls—or even minds—using nothing but sound?…
-
They Found a Lost City Beneath the Pyramids… And It Changes Everything We Know About History
🌍 Table of Contents 🏛️ Introduction: A Hidden City Awakes For generations, the Great Pyramids of Giza have captivated the world. But…